23 Dec19:41pm
Nanbiosis
Antibody purification
Antibody purification involves the selective enrichment or specific isolation of antibodies from various sources, such as serum (for polyclonal antibodies), or cell culture supernatant (for monoclonal antibodies).
The main methods used for antibody purification are:
- Physicochemical Fractionation: This method includes differential precipitation, size-exclusion, or ion exchange chromatography, based on size, charge, or other shared chemical characteristics It separates proteins that includes the immunoglobulins (antibodies) based on size, charge, or other shared chemical characteristics
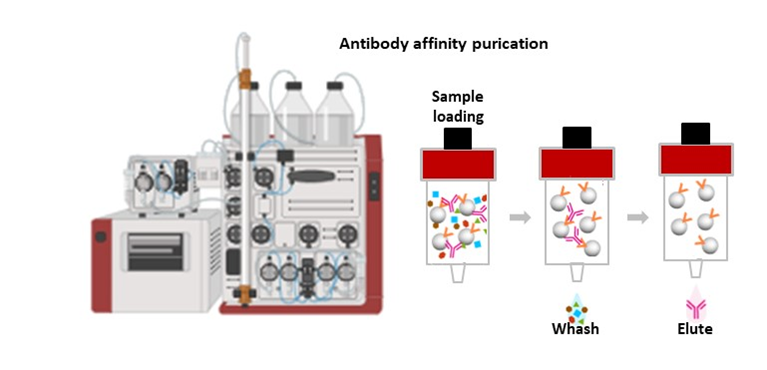
- Class-Specific Affinity: In this approach, specific antibody classes (e.g., IgG) are bound to solid phases using immobilized biological ligands (such as proteins A or G). This method purifies all antibodies of the target class without considering antigen specificity.
- Antigen-Specific Affinity: Here, only antibodies in a sample that bind to a particular antigen are purified. Affinity chromatography is performed using a column packed with immobilized antigen (the same antigen used for immunization). Only antibodies that bind to the antigen are isolated. This method provides a higher yield of antigen-specific antibodies than Protein A/G affinity chromatography, though the total amount of recovered antibodies is lower.
Customer benefits
- High Purity: Antibody purification ensures that the isolated antibodies are of high purity, minimizing contamination by other proteins.
- Specificity: By using antigen-specific affinity purification, researchers obtain antibodies that specifically recognize their target antigen.
- Consistent Results: Purified antibodies lead to more consistent and reliable experimental results.
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: Purified antibodies are essential for diagnostic assays, therapeutic development, and research applications.
- Quality: We operate under ISO 9001 quality standards, ensuring consistent, reliable antibody production.
Target customer
- Research Institutions: Universities, research centers, and laboratories engaged in biomedical research.
- Biotech Companies: Organizations involved in drug discovery, diagnostics, and therapeutic development.
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Those working on antibody-based therapies or vaccines.
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals and clinics conducting specialized research.
- Food & Environmental Quality Control Companies: Entities involved in:
- Food Contaminant Detection: Developing antibody-based tests for identifying foodborne pathogens and toxins.
- Environmental Contaminant Detection: Creating antibody-based assays for detecting environmental pollutants in air, water, and soil.
Additional information
Selected references:
- Giovanna Roncador; Pablo Engel; Lorena Maestre; et al; Alison H.Banham., Nuria Pascual 2016. The European antibody network’s practical guide to finding and validating suitable antibodies for research. mAbs. Taylor & Francis Online. 8-1, pp.27-36.
- B. Rodriguez-Urretavizcaya, N. Pascual, C. Pastells, M. T. Martin-Gomez, Ll. Vilaplana, M.-P. Marco. Diagnostic and Stratification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infected Patients by Immunochemical Quantitative Determination of Pyocyanin from Clinical Bacterial Isolates. Frontiers in Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 11, 786929, 2021. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.786929








