Biomaterials as signal-releasing platforms
Scientists of the CIBER-BBN and IBEC reserch group Biomaterials for Regenerative Therapies, led by Miguel Angel Mateos-Timoneda and Elisabeth Engel who run NANBIOSIS U5. Rapid Prototyping Unit, have published a review of the state-of-the-art in biomaterials for skin healing that proposes a move towards more personalized, in situ therapies.
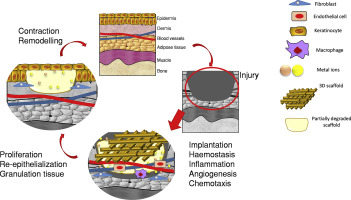
Skin wound healing repairs and restore tissue through a complex process that involves different cells and signalling molecules that regulate cellular response and the remodelling of the extracellular matrix. Publishing in Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, the article begins by summarizing recent advances in therapies for healing that combine biomolecule signals such as growth factors and cytokines with cells.
“So far, the application of these therapies is hampered by high costs, a lack of standardization, no scalable processes, and storage and regulatory issues – as well as a lack of real evidence that they work,” explains Oscar Castaño, senior researcher in the group. “To address this, we suggest concentrating on biomaterials that can act as platforms to generate stimuli that can promote the type of cell activity that encourages skin regeneration.” This strategy of tissue regeneration in situ uses the body’s own capacity for regeneration by mobilizing host endogenous stem cells or tissue-specific progenitor cells to the wound site to promote repair and regeneration. “The aim would be to create instructive microenvironments that combine biomaterial supports with the many different signal cues that happen in wound healing,” says Oscar. “They’d regulate the spatio-temporal delivery of the proper signalling based on the biological mechanisms of the various events that occur.”
Article of reference:
Oscar Castaño, Soledad Pérez-Amodio, Claudia Navarro-Requena, Miguel Angel Mateos-Timoneda, Elisabeth Engel Instructive microenvironments in skin wound healing: Biomaterials as signal releasing platforms. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 129, 95-117, 2018. doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.03.012