Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM): Principles, Modes, and Emerging Applications in Nanotechnology and Biomedicine
Discover how Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) provides nanometric precision in imaging, mechanical analysis, and electrochemical characterization of surfaces. Explore real-world applications in nanotech, semiconductors, and biomedicine.
Introduction
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is a cutting-edge surface characterization technique that enables researchers to explore surfaces with nanometer-scale precision. Unlike optical or electron microscopes, AFM uses a mechanical probe to scan and measure the surface topography, material properties, and interactions at the atomic level.
The versatility of AFM allows it to operate in various environments, including air, vacuum, and liquids. This makes it ideal for a wide range of applications, from materials science to biomedicine. It provides both qualitative imaging and quantitative analysis of topography, mechanical elasticity, electrical properties, and more.
As advanced as it is adaptable, AFM enables the development of new semiconductors, high-performance polymers, bio-compatible coatings, and real-time biological measurements at the molecular scale. With the integration of specialized modes and AI-driven software, the Bruker Dimension Icon-PT AFM, for example, brings even greater efficiency and precision to modern nanoscale research.
Understanding the fundamentals of AFM
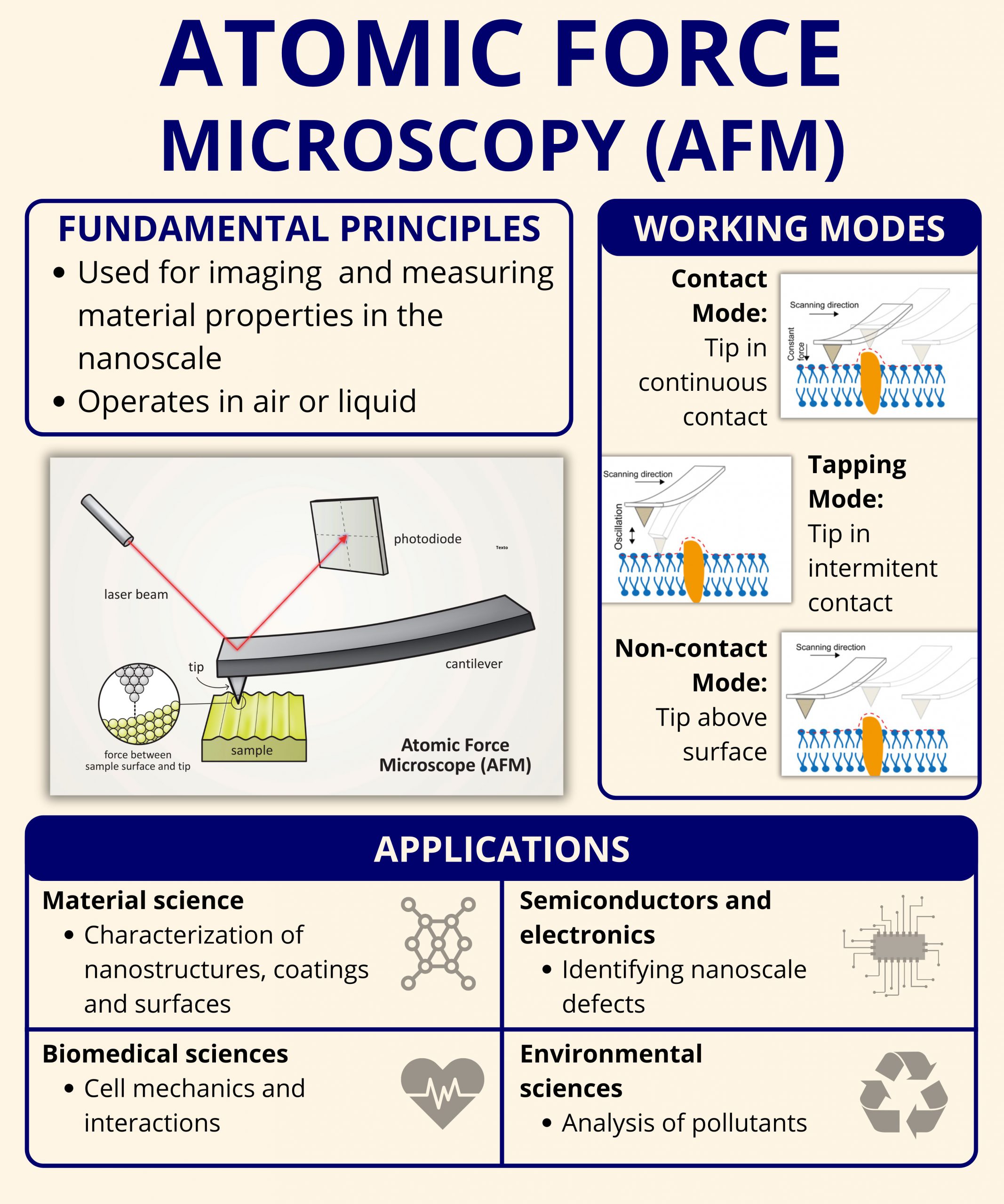
Atomic Force Microscopy was invented in 1986 by Binnig, Quate, and Gerber. Its original design has since evolved into a family of techniques that share one common feature: the interaction between a sharp probe tip and a surface.
The basic components of an AFM system include:
- Cantilever and Tip: A nanometer-scale tip mounted on a flexible cantilever that interacts with the sample.
- Laser and Photodetector: A laser beam reflects off the back of the cantilever and onto a photodetector, tracking vertical displacement.
- Piezoelectric Scanner: Controls the movement of the sample or the probe with sub-nanometer accuracy.
- Feedback System: Maintains a constant force or height to allow precise mapping of the surface.
AFM does not rely on light or electrons to generate images. Instead, it uses force interactions, such as van der Waals, electrostatic, or capillary forces, to sense the features of the surface. This makes it especially suitable for non-conductive samples, unlike SEM or TEM.
Additionally, AFM can function in air, liquids, or controlled gas environments, enabling real-time biological and chemical analysis under near-physiological conditions. This environmental adaptability is a major advantage in biosanitary research.
AFM working modes explained
Atomic Force Microscopy offers multiple operational modes, each designed for specific material types and analytical goals.
Contact Mode
In contact mode, the probe remains in constant contact with the surface as it scans. This mode provides high-resolution imaging but can be invasive, especially for soft or biological samples. It is best suited for hard, stable surfaces such as metals, glass, and ceramics.
Tapping Mode (Intermittent contact)
Tapping mode oscillates the cantilever at its resonance frequency and gently touches the surface during each cycle. This reduces lateral forces and sample damage, making it ideal for imaging soft polymers, biological tissues, and loosely bound nanoparticles.
Non-contact Mode
In non-contact mode, the cantilever vibrates near the surface without touching it. It detects attractive van der Waals forces, offering the least invasive method for delicate or loosely bound surface features.
Other advanced Modes
In addition to the former, there are advanced AFM modes worth mentioning, such as PeakForce QNM®, KPFM, and TUNA.
- PeakForce QNM®: Measures mechanical properties (modulus, adhesion, deformation) at <1 nN forces with nanometric resolution.
- Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy (KPFM): Maps electrostatic surface potential and work function.
- TUNA/CAFM: Enables current mapping for electrical conductivity in semiconductors and nanomaterials.
These advanced modes enable multi-parameter surface mapping in a single scan, drastically improving data acquisition and analysis capabilities.
Applications of Atomic Force Microscopy by industry
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
AFM is pivotal in analyzing nanostructured materials, thin films, composites, and coatings. It provides:
- High-resolution topographic maps.
- Mechanical characterization (Young’s modulus, hardness, adhesion).
- Analysis of wear and deformation under mechanical stress.
This information helps design advanced materials with tailored surface properties for aerospace, electronics, and energy applications.
Biomedical and Biosanitary applications
In biomedical research, AFM reveals cellular structures, measures membrane stiffness, and observes molecular binding forces in real-time. It is used to:
- Differentiate between healthy and cancerous cells based on viscoelastic properties.
- Study protein aggregation and receptor-ligand binding.
- Investigate bacterial adhesion and extracellular matrix mechanics.
The ability of AFM to function in liquid environments is crucial for maintaining live cell conditions during measurements.
Semiconductor and Electronics
AFM is indispensable for analyzing surface defects, roughness, and conductive pathways at the nanometer level in integrated circuits (ICs), MEMS devices, and photovoltaic materials. Modes like KPFM and TUNA are used to:
- Measure nanoscale electrical conductivity.
- Characterize dielectric breakdown.
- Map doping profiles.
Environmental and Surface Chemistry
AFM is increasingly applied to study microplastics, nanotoxicology, and pollutant detection in air, soil, and water. It is used to:
- Visualize particle morphology.
- Measure surface energy and adhesion.
- Detect chemical functional groups with techniques like CFM and AFM-IR.
Comparative analysis: AFM vs. other microscopy and measurement techniques
| Technique | Key Strengths | Limitations |
| AFM | Nanoscale topography, mechanical & electrical analysis in ambient conditions | Slower scan speed, limited subsurface analysis |
| SEM | High-resolution imaging of conductive materials | Requires vacuum and coating, limited for biological samples |
| TEM | Atomic resolution, internal structure imaging | Expensive, complex sample preparation |
| Nanoindentation | Quantitative mechanical properties | Lacks spatial resolution of AFM |
| Optical Profilometry | Fast, non-contact surface mapping | Poor vertical resolution below 100 nm |
AFM stands out due to its versatility and resolution, especially when used for multi-modal surface characterization.
Challenges and barriers to adoption of AFM
Despite its advantages, AFM adoption faces several challenges:
- High equipment costs: Advanced AFM systems are expensive, making them inaccessible for routine labs.
- Complexity: Requires expert operators to run the system and interpret data.
- Scanning time: Slower than optical or SEM techniques, especially for large areas.
- Sample preparation: Soft or uneven samples may deform under probe interaction.
- Data volume: Generates massive datasets that require sophisticated analysis tools.
Ongoing improvements in automation, software, and user interface design aim to lower these barriers and broaden AFM accessibility. More importantly, the use of expert personnel and speciallized facilities overcomes most of these drawbacks. To learn more, visit Unit 16 of NANBIOSIS: Surface Characterisation and Bacterial Colonization Unit.
Future trends and innovations in AFM
High-Speed AFM and automation
Emerging high-speed AFMs reduce scan times significantly, enabling near real-time visualization of dynamic biological and chemical processes. AI-powered analysis accelerates interpretation and enhances reproducibility.
AFM for Drug Delivery and molecular manipulation
AFM enables single-molecule force spectroscopy, critical in understanding drug-target interactions. In future applications, AFM-integrated tools could guide surgeries, diagnose diseases at the nanoscale, or evaluate drug responses in real time.
Integration with robotics and quantum research
Miniaturized AFM probes embedded in surgical instruments or autonomous robots could perform in vivo diagnostics. In quantum and nanoelectronics, AFM could help design next-generation devices with atomic precision.
Future enhancements may include:
- AFM-endoscopy for cancer detection
- AI-assisted materials discovery
- Autonomous environmental nanosensors
- Nanoassembly using functionalized probes
The adaptability of this technique makes it an ideal platform for multidisciplinary innovation.
Conclusion
Atomic Force Microscopy has evolved from a niche research tool to a multi-functional powerhouse in nanotechnology, biomedicine, electronics, and environmental science. With the ability to deliver atomic-scale resolution, multi-modal characterization, and operation under diverse conditions, AFM is shaping the future of materials research and nanoscale innovation.
Despite technical and financial barriers, ongoing developments in probe technology, high-speed scanning, and AI integration are making AFM more accessible and efficient than ever. From studying living cells to engineering quantum devices, AFM is, and will remain, one of the most transformative tools in modern science.
Credits:
Margarita Hierro Oliva
Gabriel Alfranca
What is NANBIOSIS?
The goal of NANBIOSIS is to provide comprehensive and integrated advanced solutions for companies and research institutions in biomedical applications. All of this is done through a single-entry point, involving the design and production of biomaterials, nanomaterials, and their nanoconjugates. This includes their characterization from physical-chemical, functional, toxicological, and biological perspectives (preclinical validation).
In order to access our Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions with priority access, enter our Competitive Call here.
NANBIOSIS has worked with pharmaceutical companies of all sizes in the areas of drug delivery, biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Here are a few of them: