Researchers of BSICoS Group and NANBIOSIS ICTS U27 High Performance Computing from CIBER-BBN and I3A-UZ have published a new article in the scientific journal IEEE Transactions Biomedical Engineering. proposing a new method to estimate tidal volume during stress test based only on the electrocardiogram signal.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) has been regarded as a source of respiratory information with the main focus in the estimation of the respiratory rate. Although little research concerning the estimation of tidal volume (TV) has been conducted, there are several ECG-derived features that have been related with TV in the literature, such as ECG-derived respiration, heart rate variability or respiratory rate.
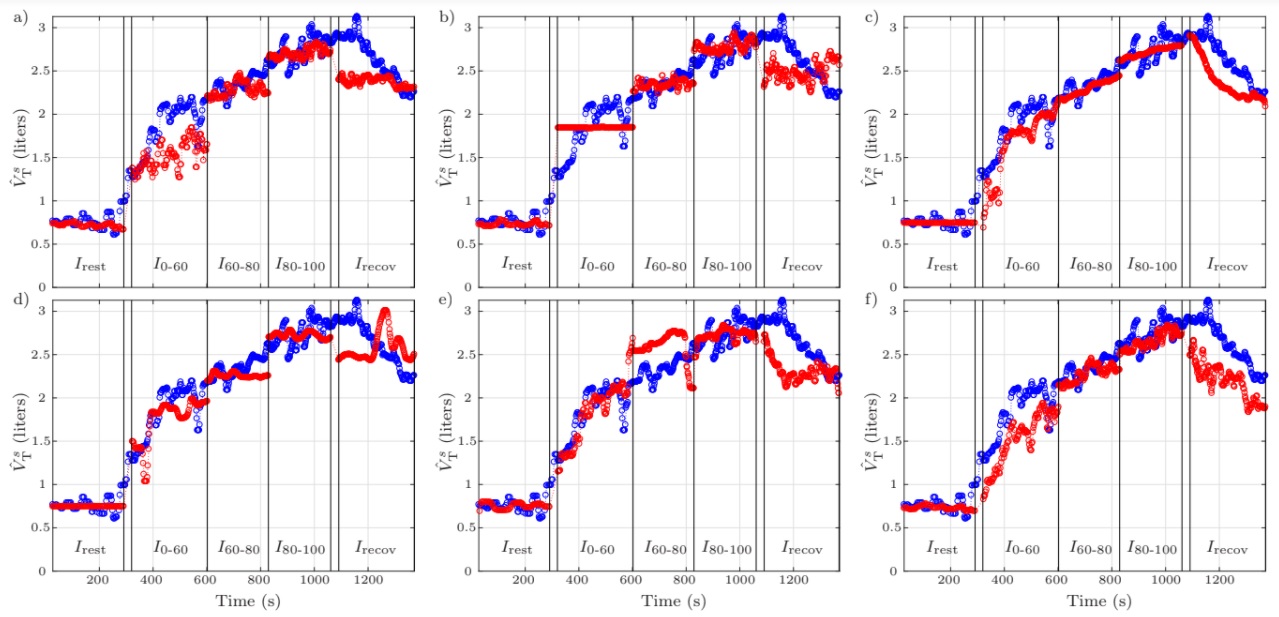
In this work, resarchers exploited these features for estimating TV using a linear model. 25 young (33.4 ± 5.2 years) healthy male volunteers were recruited for performing a maximal (MaxT) and a submaximal (SubT) treadmill stress test, which were conducted in different days. Both tests were automatically segmented in stages attending to the heart rate. Afterwards, a subject-specific TV model was calibrated for each stage, employing features from MaxT, and the model was later used for estimating the TV in SubT.
During exercise, the different proposed approaches led to relative fitting errors lower than 14% in most of the cases and than 6% in some of them. Low achieved fitting errors suggest that TV can be estimated from ECG during a treadmill stress test. The results suggest that it is possible to estimate TV during exercise using only ECG-derived features.
Article of reference:
Milagro, J; Hernando, D; Lázaro, J; Casajús, J A; Garatachea, N; Gil, E; Bailón, R. Electrocardiogram-Derived Tidal Volume During Treadmill Stress Test
IEEE Transactions Biomedical Engineering, 67 (1), 2020. DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2911351








