1st Nanomedicine Forum of CIBER-BBN/NANBIOSIS and CSIC Nanomed Conection
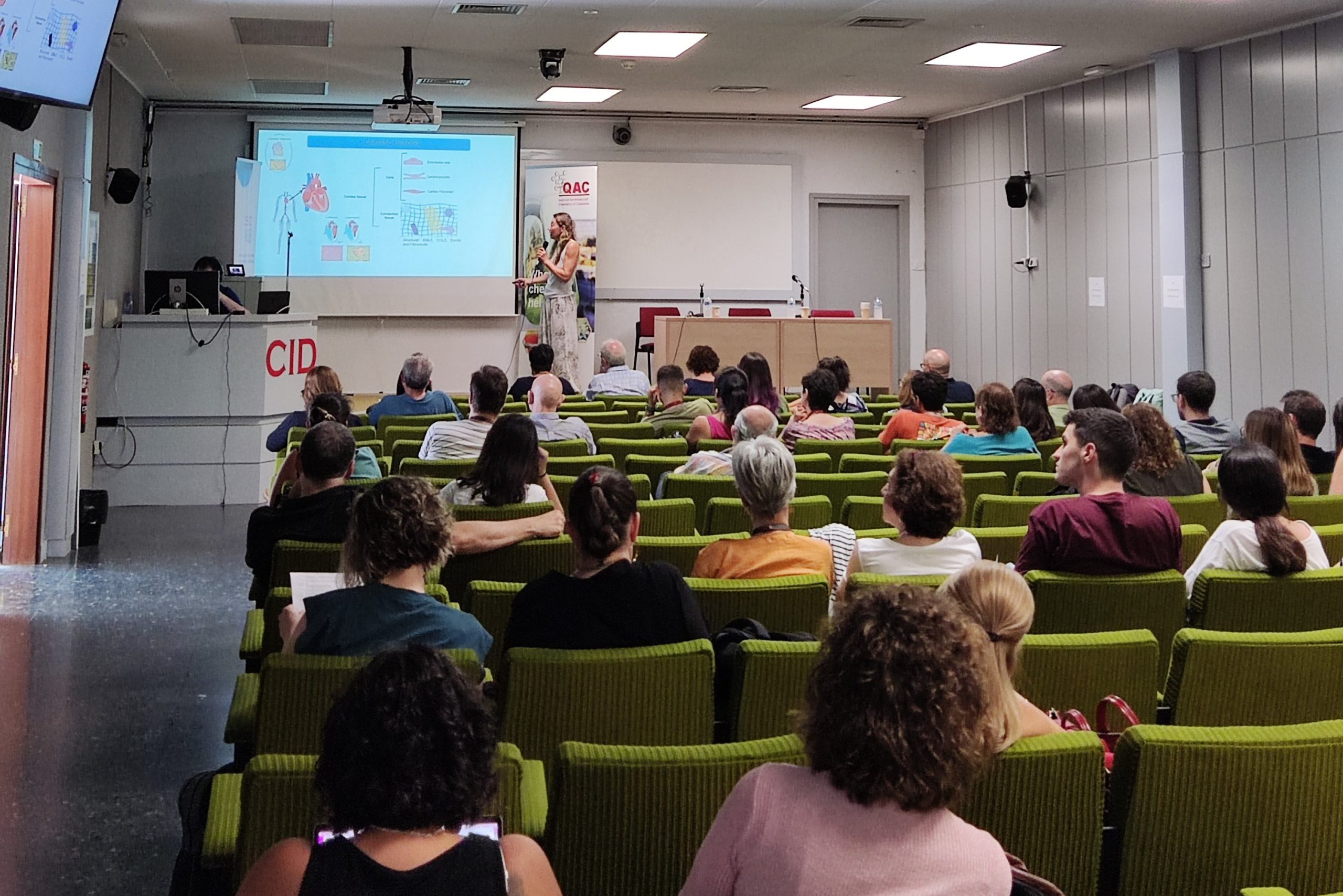
During the days 30 of June and 1st of July took place in Barcelona, in the auditorium of the Institute of Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC), the 1st Forum on Nanomedicine gathering scientists from the CSIC net Nanomed Conection and from the CIBER-BBN and its ICTS NANBIOSIS.
This forum brought toguether researchers from the most eminent national research centers in nanomedicine, that during the two days meeting presented their works and findings and discussed the impact of nanomedicine in the fields of drug delivery, diagnosis and therapy.
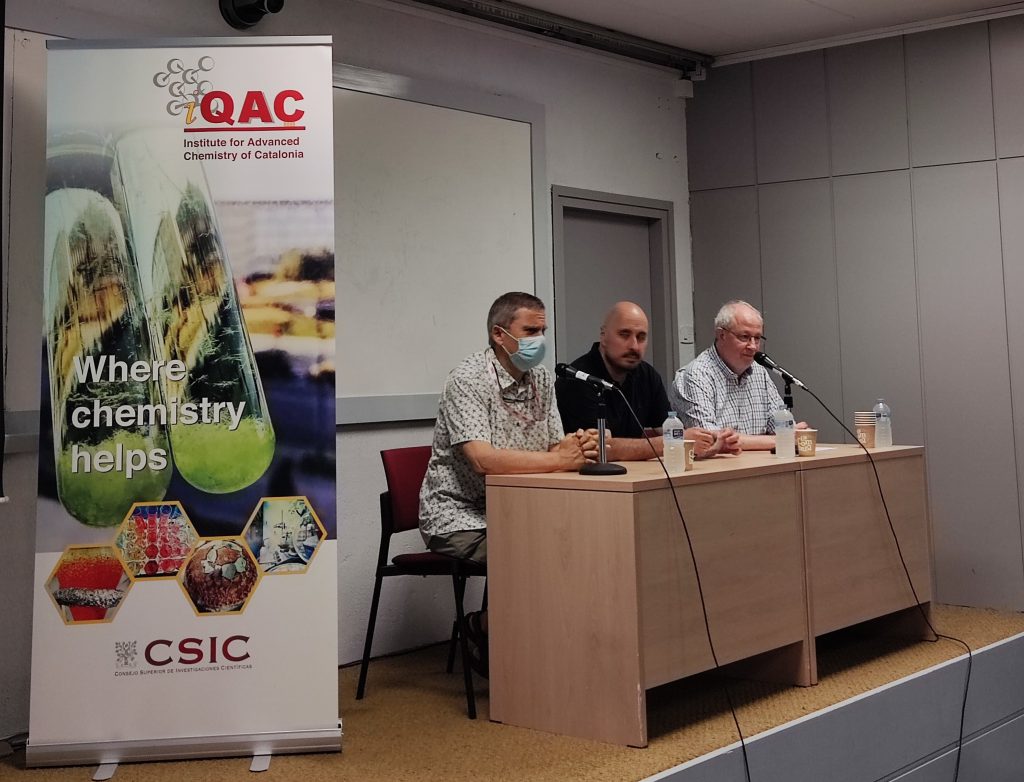
The workshop was open by the Director of IQAC-CSIC, Jesús Joglar, the Scientific Coordinator of Nanomed Conection, Fernando Herranz, and the Scientific Director of CIBER-BBN, Ramón Martínez Máñez.
18 research groups gave their talks distributed in four sessions:
- Nanobiotechnological solutions for diagnosis and therapy
- Drug delivery nanosystems
- Applications for oncology
- Nanomedicine & other frontier applications
The presentations aroused great interest and futher debate among the attendees present in the auditorium (around 50) and the on line participants (The event was also broadcast online previous registration with more than 125 registrations received).
The videos of the presentations will be soon available in the NANBIOSIS youtube channel.
Here we highlight the eight talks by researchers from NANBIOSIS units:
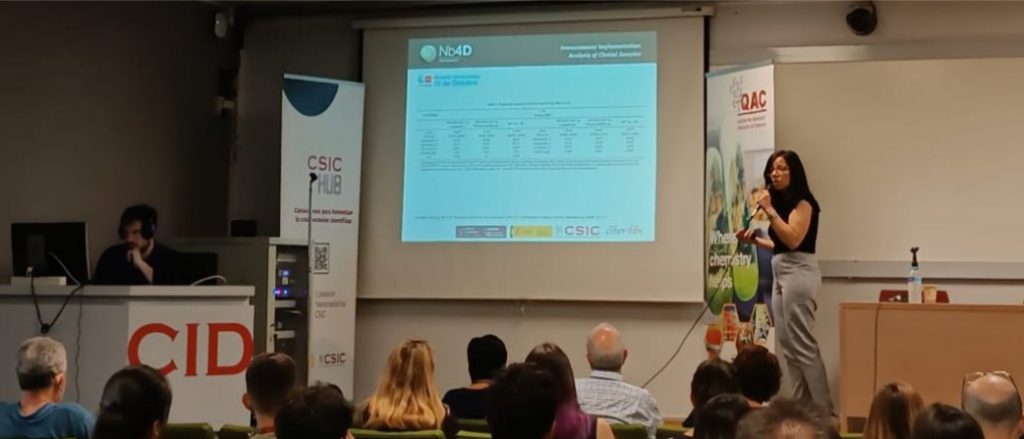
The first session of Nanobiotechnological solutions for diagnosis and therapy, started with the talk by Montserrat Rodríguez from Nb4D group – NANBIOSIS U2 CAbS, from CIBER-BBN and IQAC-CSIC, entitled “Targeting aromatic amino acid metabolism for the early diagnosis of neurological diseases”, presenting their results on in vitro samples, on thermal power characterization experiments to study the thermal efficiency of non-sinusoidal stimulation and on efficiency characterization experiments in cell cultures with cancer cell liness.
Also in this session chaired by Miriam Royo, Scientific Coordinator of NANBIOSIS U3 Synthesis of Peptides Unit of CIBER-BBN and IQAC-CSIC, took place an interesting and passionate talk by Ramón Eritja, Scientific Director of NANBIOSIS U29 Oligonucleotide Synthesis Platform (OSP),
In the last years, interest in therapeutic applications of oligonucleotides has increased enormously, especially after the development of messenger RNA vaccines in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this way, metabolic diseases such as dyslipidemia and hereditary diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy have been successfully addressed. The NANBIOSIS Oligonucleotide Synthesis Platform (OSP) focuses on the design, synthesis and characterization of modified oligonucleotides, in order to enhance the therapeutic properties of the oligonucleotides and to improve the control of gene expression. Ramon Eritja presented their most recent results in the development of new conjugates with antiproliferative activity and in the design of DNA probes for the detection of viral genomes.
In the session of “Nanomedicine and other frontiers applications”, chaired by María del Puerto Morales Herrero (ICMM-CSIC), Elena Martínez Fraiz, from the Nanobioengineering group of CIBER-BBN and IBEC running NANBIOSIS Unit 7 of Nanotechnology, presented a nanostructured surface able to produce multivalent effects of surface-bound ephrinB1 ligands on the dynamics of oligomerization of EphB2 receptors whic can benefit applications such as the design of new bioactive materials and drug-delivery systems.
The session of Drug delivery nanosystems, chaired by Ramón Martínez Máñez, began with the talk by Vanessa Díaz Riascos, presesnting the in vivo efficacy, biodistribution and toxicity testing of nanomedicines at NANBIOSIS U20 FVPR, of CIBER-BBN and VHIR, explaining how their texting expertise and their in vivo and ex vivo fluorescence imaging techniques facilitate a rapid and efficient preclinical development of candidates, reducing considerably the time and costs of conventional developments.
Santiago Grijalvo Torrijo, from NANBIOSIS U12 Nanostructured liquid characterization unit expoke about Nano-emulsion-derived polymeric carriers for biomedical applications also discussing the impact of the protein corona on colloidal stability, antioxidant activities, cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of drug-loaded nanoparticles.
Antoni Llopis Lorente, (NANBIOSIS U26 NMR: Biomedical Applications II), expoke about Gated silica nanoparticles for controlled release. Chemical communication, based on the exchange of molecules as messengers, allows different entities to share information, cooperate and orchestrate collective behaviors. Communication using chemical messengers (such as neurotransmitters, hormones and pheromones) is the main way of communication across the natural world; yet engineering chemical communication between micro/nanosystems is a key emergent topic in micro/nanotechnology, biomimicry and related areas. Santiago explainined recent progress by their group in the development of engineered particles for chemical communication and nanomedicine applications.
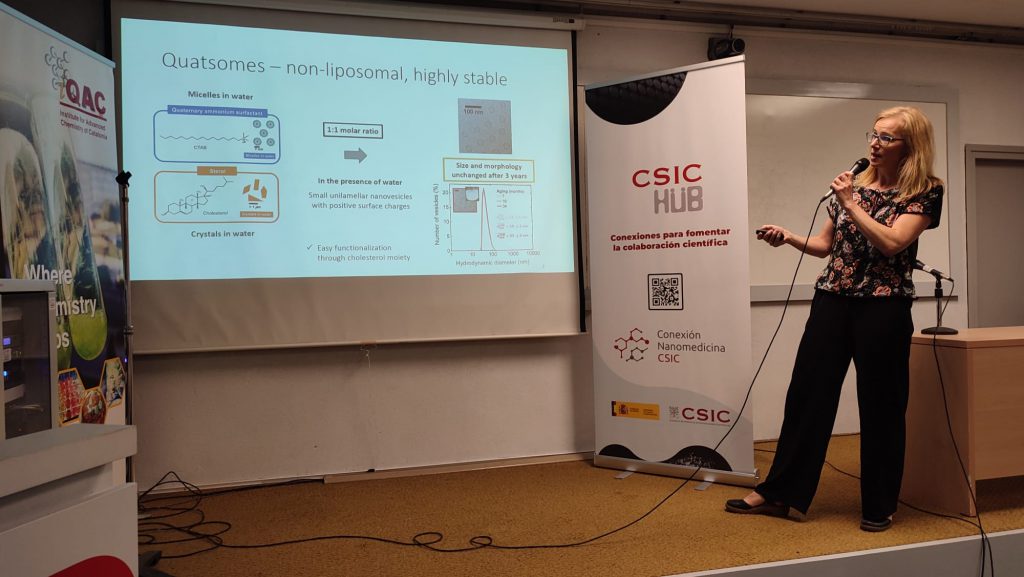
And closing the session, Mariana Köber (Nanomol Group –NANBIOSIS U6 of Biomaterial Processing and Nanostructuring Unit from CIBER-BBN and ICMAB-CSIC) gave a talk on Quatsomes as versatile nanovesicles for biomedical applications.
In the session of Applications for Oncology, Pilar Martín Duque from NFP group – NANBIOSIS U9 Synthesis of Nanoparticles Unit of CIBER-BBN and INMA-CSIC, gave a very interesting talk explained their approach and recent progress on the search of trojan horses for an improved theragnosis of cancer.
Here we want to thank the Institute of Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) for hosting this event and for the help in its preparation and development.