New 3D culture device to better understand how tumours work
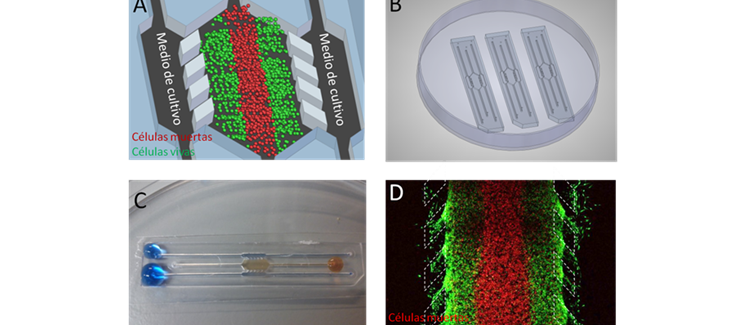
Scientist of NANBIOSIS in collaboration with other CIBER-BBN researchers have developed a sophisticated microfluidic biomedicine device capable of reproducing in vitro and by 3D bioprinting the complexity of different tumour types. This device allows tumour cells to grow in a 3D environment where nutrients and oxygen are supplied in a controlled way through small capillaries, thus mimicking the body’s own blood vessels.
Thanks to this new technology, it is now possible to reproduce in a controlled way all the processes of the tumour environment, which could help to develop new treatments and combinations of drugs that are more effective for the treatment of these tumours.
In this study, published in Scientific Reports, have participated researchers from the Group of Applied Mechanics and Bioengineering (AMB) of the University of Zaragoza , which coordinates Unit 13 of NANBIOSIS .
Article of reference:
Development and characterization of a microfluidic model of the tumour microenvironment.Jose M. Ayuso, María Virumbrales-Muñoz, Alodia Lacueva, Pilar M. Lanuza, Elisa Checa-Chavarria, Pablo Botella, Eduardo Fernández, Manuel Doblare, Simon J. Allison, Roger M. Phillips, Julián Pardo, Luis J. Fernandez e Ignacio Ochoa. Scientific Reports. 10.1038/srep36086