Nanotechnology to slow down the growth of glioblastomas
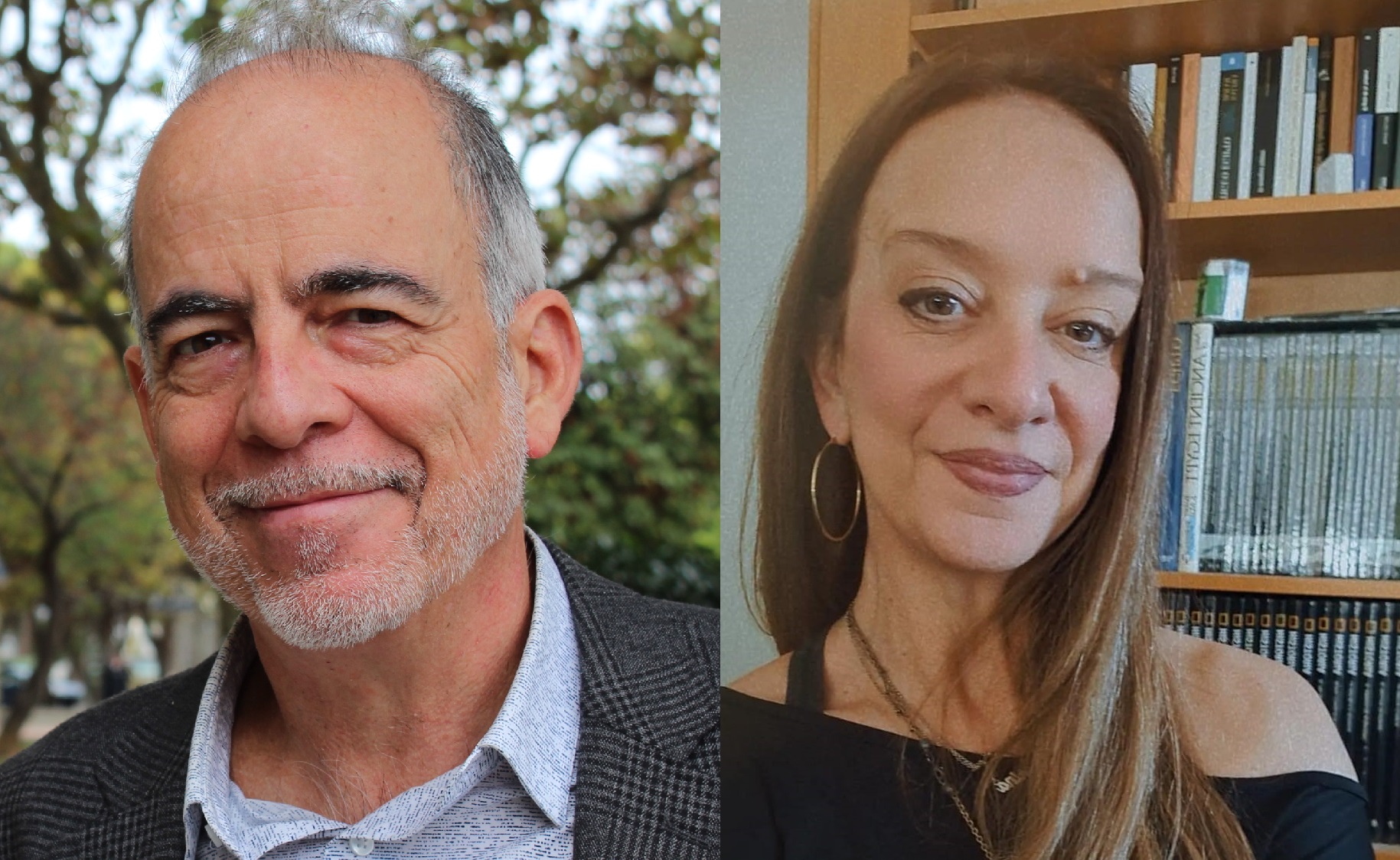
Directors of Unit 20 and Unit 3, Ibane Abasolo and Miriam Royo, show us the ReachGlio project, which uses nanomedicines to slow glioblastoma growth by targeting tumors in the brain, improving drug delivery through nanoparticles.
Barcelona, october 2024. Each year, on October 9th, Nanotechnology Day is celebrated, a discipline dedicated to understanding and utilizing matter at a nanometric scale for purposes such as industrial or medical applications. Nanotechnology plays a fundamental role in many research lines developed at the Institute for Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) and the Vall d’Hebron Research Institute (VHIR).
“Our goal is to propose one or more clinical trials in patients with glioblastoma using nanomedicines that can efficiently reach the brain and have antitumor activity.”
— Dr. Ibane Abasolo
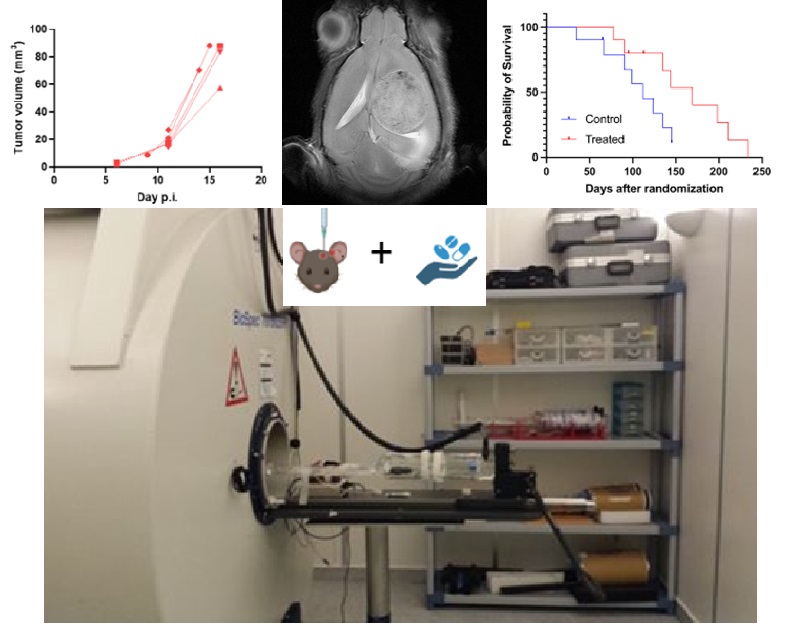
One of the standout projects in this area is the ReachGlio project, which focuses on improving drug delivery designed to slow the growth of glioblastomas using multifunctional nanomedicines. “Our goal is to propose one or more clinical trials in patients with glioblastoma using nanomedicines that can efficiently reach the brain and have antitumor activity,” explains Ibane Abasolo, the project’s principal investigator.
ReachGlio is part of the TRANSCAN 3 program, involving seven European entities, including two Spanish institutions: the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) and the Biomedical Research Networking Center in Bioengineering, Biomaterials, and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN). The Institute for Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) and the Vall d’Hebron Research Institute (VHIR) participate through the CIBER-BBN groups led by researchers Miriam Royo and Ibane Abasolo.
Nanomedicines with antitumor activity
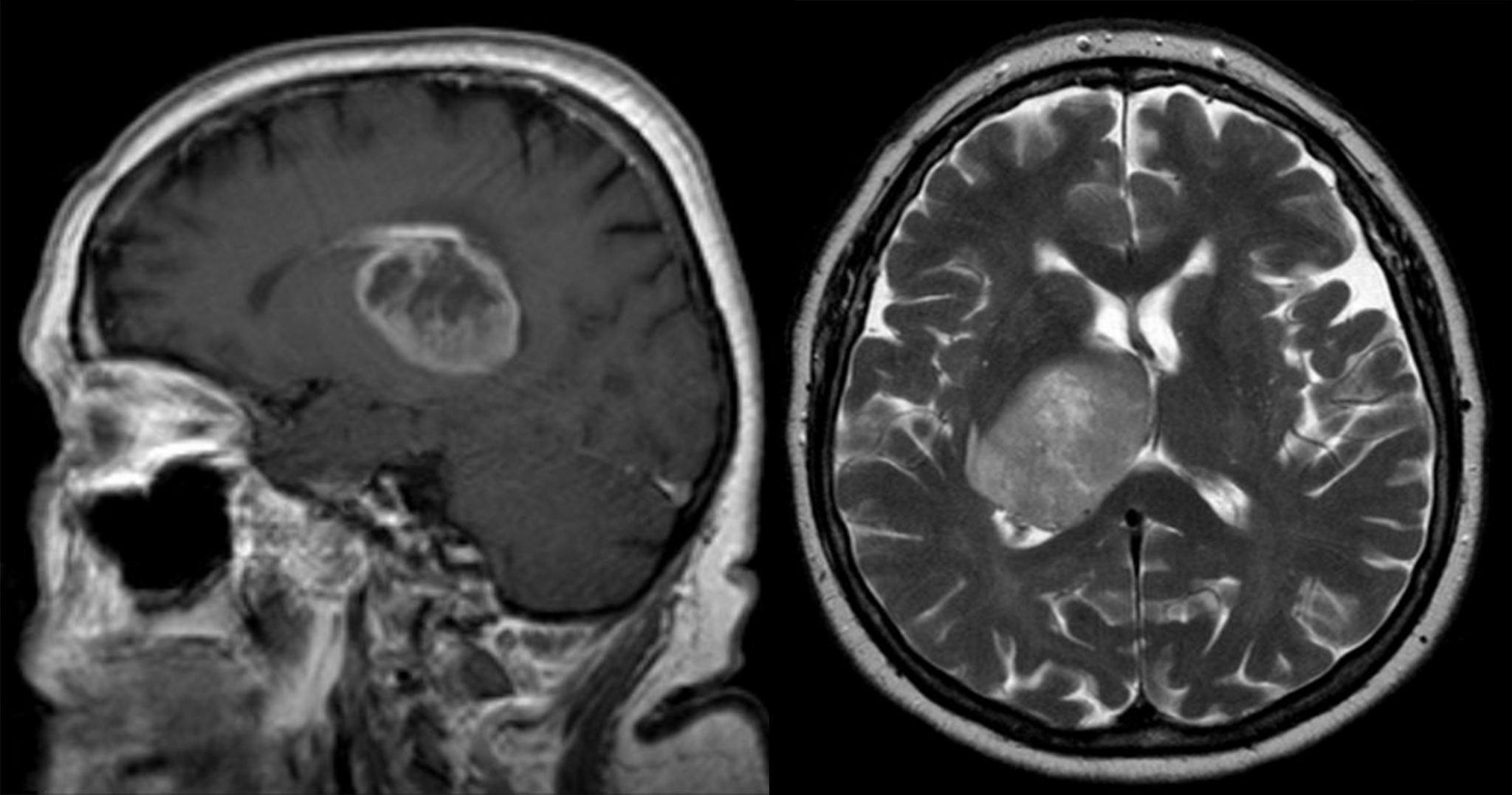
Glioblastomas are among the most aggressive tumors due to their location within the brain and their ability to invade surrounding tissue. Additionally, they are highly heterogeneous tumors. All of this explains why the prognosis for patients with this type of tumor remains very poor, with no curative therapy options available.
“One of the main challenges for drugs designed to slow the growth of glioblastomas is how difficult it is for them to effectively reach the brain and distribute homogeneously within such a diverse tumor,” explains Miriam Royo, researcher of the project.
“One of the main challenges for drugs designed to slow the growth of glioblastomas is how difficult it is for them to effectively reach the brain and distribute homogeneously within such a diverse tumor.”
— Dr. Miriam Royo
To overcome this obstacle, the current project proposes the use of nanoparticles that incorporate existing drugs, which, although they have already proven capable of slowing tumor cells, have difficulty accessing the brain. These nanoparticles, specifically polymeric micelles, have small peptide sequences on their surface that act as targeting molecules. These peptides help the nanoparticles cross the blood-brain barrier, between the blood vessels and the brain, and once inside the brain, they guide them towards the tumor cells.
During the project, a drug (NGR-TNF) will also be tested, which makes the blood-brain barrier more permeable, in combination with antitumor treatments or the nanomedicines being developed. “This specific part is planned to be tested at the veterinary level in dogs that already suffer from spontaneous brain tumors, so we hope the project’s results can quickly reach glioblastoma patients,” adds Ibane Abasolo.
References:
What is NANBIOSIS?
The goal of NANBIOSIS is to provide comprehensive and integrated advanced solutions for companies and research institutions in biomedical applications. All of this is done through a single-entry point, involving the design and production of biomaterials, nanomaterials, and their nanoconjugates. This includes their characterization from physical-chemical, functional, toxicological, and biological perspectives (preclinical validation).
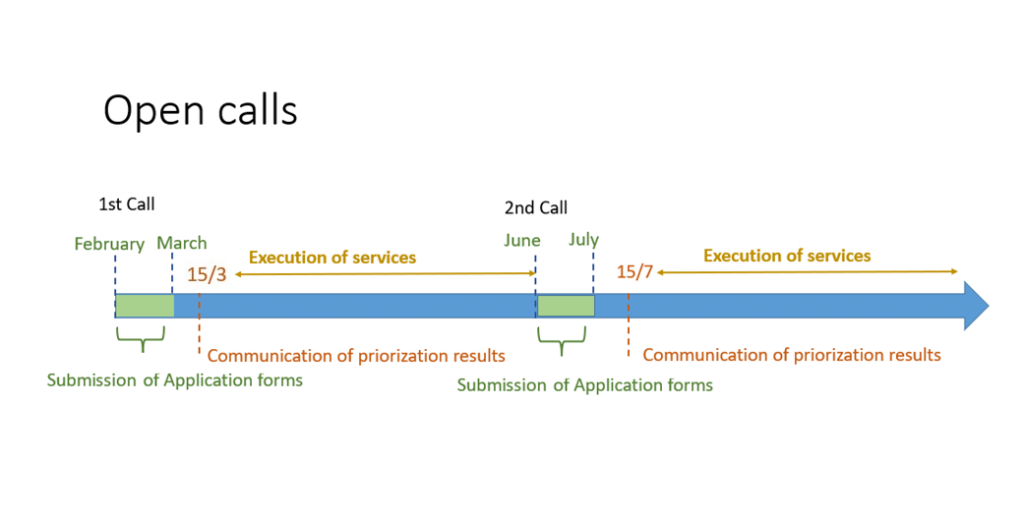
In order to access our Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions with priority access, enter our Competitive Call here.
NANBIOSIS has worked with pharmaceutical companies of all sizes in the areas of drug delivery, biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Here are a few of them: