NANBIOSIS contributes to innovative protein granules for new biomedical applications
Researchers from NANBIOSIS co-author a new study showcasing an innovative approach to protein-based biomaterials for drug delivery and regenerative medicine.
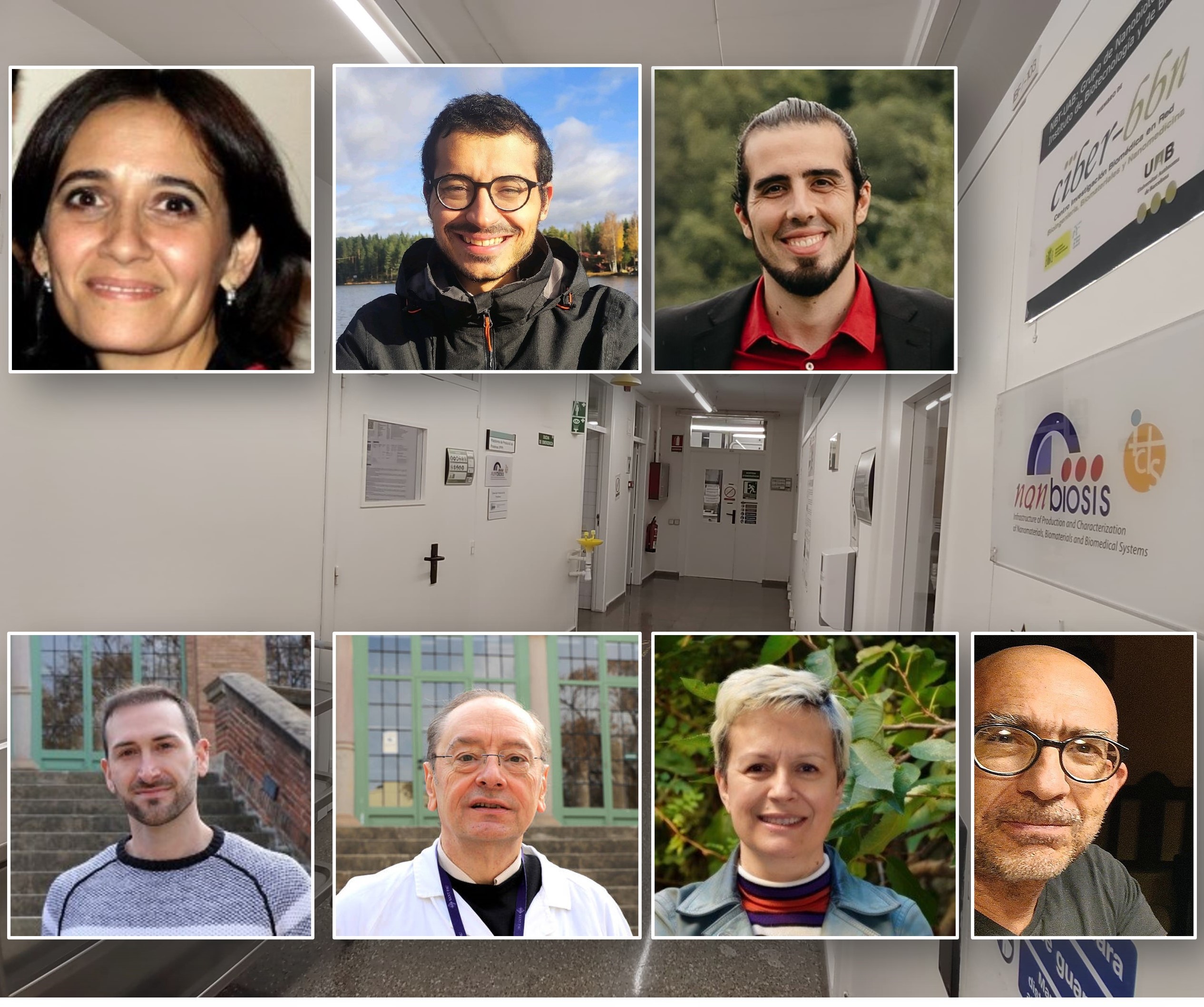
Barcelona, april 2025. A recent publication in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules highlights the cutting-edge work of scientists from Unit 1 (Protein Production Platform, PPP) and Unit 18 (Nanotoxicology Unit) of NANBIOSIS, under the leadership of Prof. Antonio Villaverde and Prof. Ramón Mangues, respectively. The study, entitled “Surpassing protein specificity in biomimetics of bacterial amyloids” (DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139635), explores the development of artificial protein granules with promising applications in biomedicine.
A Novel Approach to Biomimetic Materials
The research introduces a His-Zn²⁺-based technology to produce artificial protein microgranules that mimic the properties of natural protein depots. By promoting protein–protein interactions through histidine residues and divalent cations like zinc, the team has developed stable yet dynamic microparticles that retain the functional properties of their constituent proteins.
This biomimetic strategy enables the spontaneous formation of hybrid granules by co-aggregating distinct polypeptides. Unlike previous methods, this approach does not require structural similarity among proteins, significantly expanding its potential for versatile biomedical applications.
Cross-Unit expertise and collaboration
The study leverages the protein engineering and production capabilities of NANBIOSIS Unit 1, based at the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine (IBB), Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB). The infrastructure within this Unit and scientific expertise enabled the design, expression, and purification of the recombinant proteins used in the study.
Meanwhile, NANBIOSIS Unit 18, part of the Institut de Recerca Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (Sant Pau), contributed with advanced evaluation and nanotoxicological analysis, ensuring the functional and safe application of these newly developed biomaterials.
Potential applications in Drug Delivery and Regenerative Medicine
The artificial granules described in the paper function as multifunctional protein depots, opening new possibilities in the controlled release of therapeutic proteins and in regenerative medicine. Their hybrid nature allows for simultaneous delivery of multiple functional proteins, enhancing their potential as platforms for personalized medicine and advanced therapies.
Patent and funding
The researchers have filed a patent application to protect the novel His-Zn²⁺ aggregation technology, underlining the potential for translation to industry. The study was supported by multiple funding sources, including national and European research programs.
This research exemplifies the collaborative strength of the NANBIOSIS, where inter-Unit synergies lead to impactful discoveries in nanomedicine and biotechnology. In this case, the Protein Production Platform (Unit 1) and the Nanotoxicology Unit (Unit 18).
What is NANBIOSIS?
The goal of NANBIOSIS is to provide comprehensive and integrated advanced solutions for companies and research institutions in biomedical applications. All of this is done through a single-entry point, involving the design and production of biomaterials, nanomaterials, and their nanoconjugates. This includes their characterization from physical-chemical, functional, toxicological, and biological perspectives (preclinical validation).
In order to access our Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions with priority access, enter our Competitive Call here.
NANBIOSIS has worked with pharmaceutical companies of all sizes in the areas of drug delivery, biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Here are a few of them: