U10-S09. Characterization and development of pulmonar formulations (On-site&Remote) OUTSTANDING
Characterization and development of pulmonar formulations
Characterization and development of pulmonar formulations
3D bio-impression of scaffolding for regenerative medicine
Classic parenteral dosage forms: solutions, suspensions, emulsions,…
Parenteral dosage forms for sustained release.
Topical dossage: creams, gels,…
Classic oral dosage forms: capsules, tablets, coated tablets, microgranules,…
Oral dossages forms for suistanable release: hidrophylic matrixes, lipid matrixes, pellets,…
The techniques we use to make the pharmaceutical dosage forms are:
Customer benefits
Target customer
Additional information
The following is an example of our bioprinted materials, which were used in the first study on 3D screen printing in the fabrication of drug delivery systems:
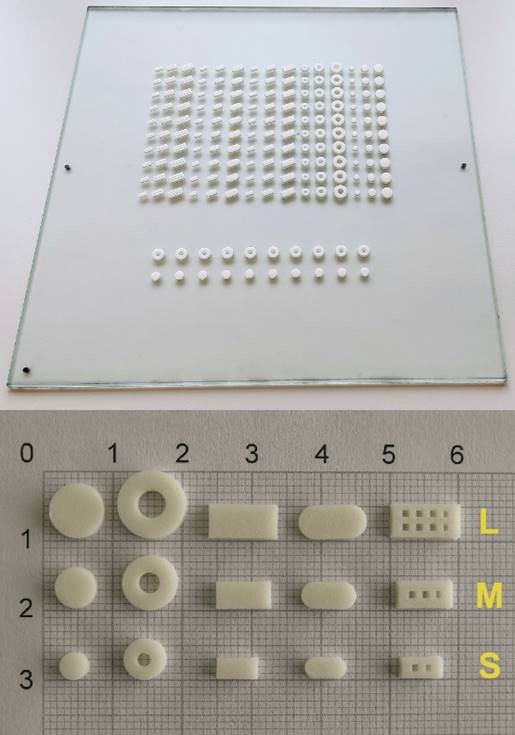
Reference: D. Moldenhauer, et al. 3D screen printing – An innovative technology for large-scale manufacturing of pharmaceutical dosage forms. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 592, 2021, 120096, ISSN 0378-5173, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120096.
Design & Development of micro- & nanocapsules for conventional drugs, peptides and proteins.
Customer benefits
Use of micro- and nanotechnologies for the design of specific formulations and capsules with conventional drugs, peptides and proteins for preclinical evaluation.
Target customer
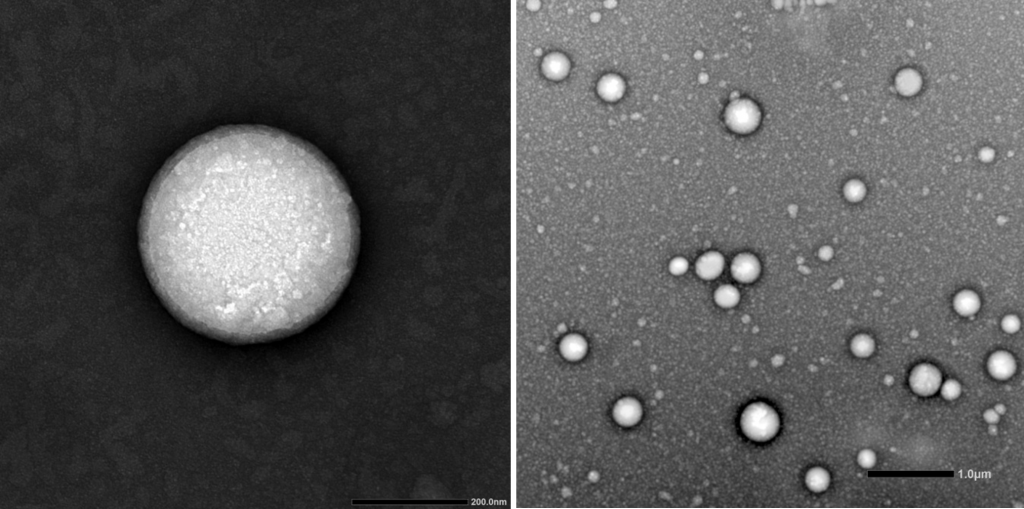
Design & Development of lipid nanoparticles to encapsulate therapeutic actives for drug delivery or gene delivery purposes: SLNs (solid lipid nanoparticles), NLCs (nanostructured lipid carriers), LNPs (self-assembled lipid nanoparticles by microfluidic technology) and niosomes.
Customer benefits
Customized elaboration of nanovehicles to deliver the therapeutic material of interest (mRNA, plasmid DNA, drugs, growth factors, peptides, antibodies…). We are specialists in designing and developing formulations for several therapeutic purposes. Among them, we develop self-assembled lipid nanoparticles, which are formed by fast microfluidic mixing in a NanoAssemblr® platform. These kinds of nanoparticles have emerged as an ideal nanotechnology approach for drug delivery and non-viral gene therapy by the high efficient encapsulation and protection of the therapeutic material from degradation. This microfluidic technology, that has been employed for COVID-19 vaccine, works under GMP conditions and enables reproducibility and scalability, which enhances its clinical translation.
Physicochemical characterization of nanovehicles, following SOPs, regarding mean particle size, polydispersity index and zeta potential. Additional parameters can be determined, such as, pH of nanoparticle suspension, microscopic morphology of the nanoparticles, encapsulation efficiency of the active principle and in vitro release profile. Optionally, biological evaluation can be performed, such as transfection efficiency analysis of non-viral nanovehicles and/or cytotoxicity assays following SOPs that include the ISO 10993-5-2019 Biological evaluation of medical devices.
Target customer
References
Additional information
Cell encapsulation in alginate based microcapsules.
Optionally, cell viability assays, metabolic activity and other phenotypic / biological studies can be carried out.
Customer benefits
Microencapsulation of cells allows their transplantation in absence of immunosuppression along a wide variety of diseases, with long retention in the engrafted tissue. This strategy improves the engraftment rate and survival of transplanted cells following implantation.
Target customer
Preclinical use for in vivo models
References
Additional information
Microencapsulated cardiospheres 10X Captured Brightfield with DM_RGB_Brightfield with DM.
