Graphene transistors as eficient transducers for electrocorticography
Researchers of Micro-Nano Technologies Unit (U8) of NANBIOSIS, are co-authors of a new paper published in Advanced Functional Materials. Neuroelectronic interfaces bridge the central nervous system to the outside world and hold great potential for functional restoration in persons with paralysis, other forms of motor dysfunction, or limb loss. Neuroscientists and neurosurgeons are thus looking for technologies that could ideally record the whole brain with a high spatial and temporal resolution. Electrocorticography (ECoG), the practice of placing arrays of large-diameter electrodes (few millimeters) directly on the cortex is the current clinical solution to obtaining brain recordings with high temporal resolution.
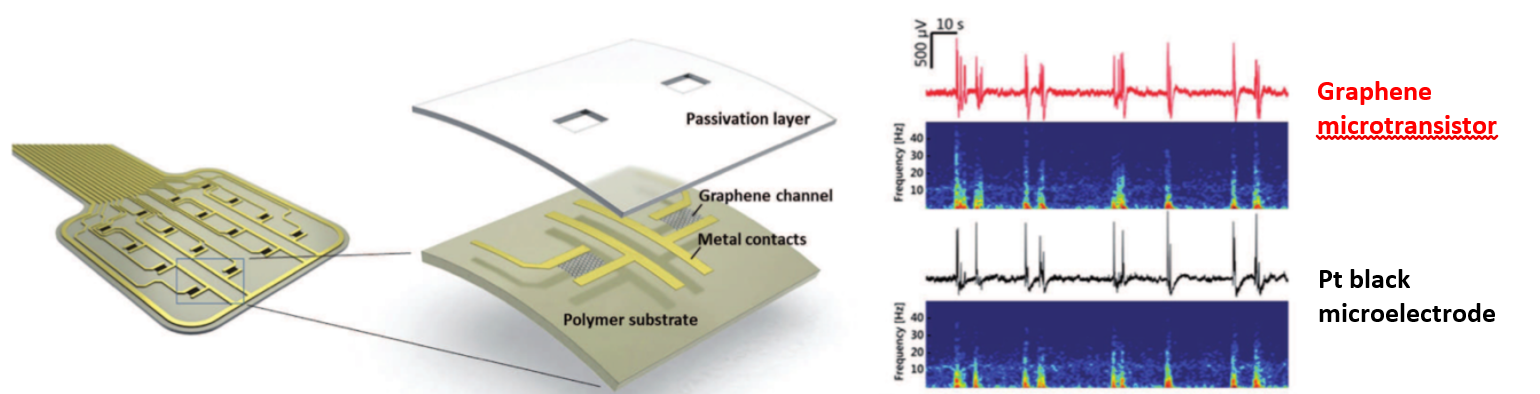
Recent research from the CIBER-BBN and IMB-CNM Biomedical Applications group (IP Rosa Villa) coordinator of NANBIOSIS Unit 8, in collaboration with ICN2 (IP JA Garrido) , IDIBAPS (IP MV Sanchez Vives) and INSERM (IP B Yvert) groups, has focused on the development of graphene technology for electrocorticography. Specifically, flexible graphene transistor arrays have been fabricated and applied to the in vivo measurement of local field potentials.
Graphene is one of the most promising material candidates for neural interfacing thanks to its biocompatibility, low dimensionality and mechanical properties. Additionally, graphene exhibits extraordinary electrical properties such as high carrier mobility and chemical stability, features that only few materials can offer therefore helping to create a very intimate interface between the tissue and the transducing system.
However, previous in vivo studies using single layer CVD graphene have used an electrode configuration. Instead, here they propose the use of a transistor configuration. The main reason for this choice is certainly the local preamplification inherent to a transistor. As a consequence, less environmental noise is picked by the device.
Their work presents a complete description of the fabrication technology, the operation of graphene solution-gated field-effect transistors (SGFET) in saline solution and of the custom characterization electronic system. The devices are finally used in in vivo experiments in which the transconductance and noise are first characterized during slow-wave activity followed by the recording of visual and auditory evoked activity as well as of synchronous activity in a rat model of epilepsy. An in-depth comparison of the signal-to-noise ratio of graphene SGFETs with that of platinum black electrodes confirms that graphene SGFET technology is approaching the performance of state-of-the art neural technologies.
Full details of the fabrication, characterization and in vivo performance of the flexible graphene transistor probes can be found in the paper below.
Hébert, C., et al., Flexible Graphene Solution‐Gated Field‐Effect Transistors: Efficient Transducers for Micro‐Electrocorticography. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017.