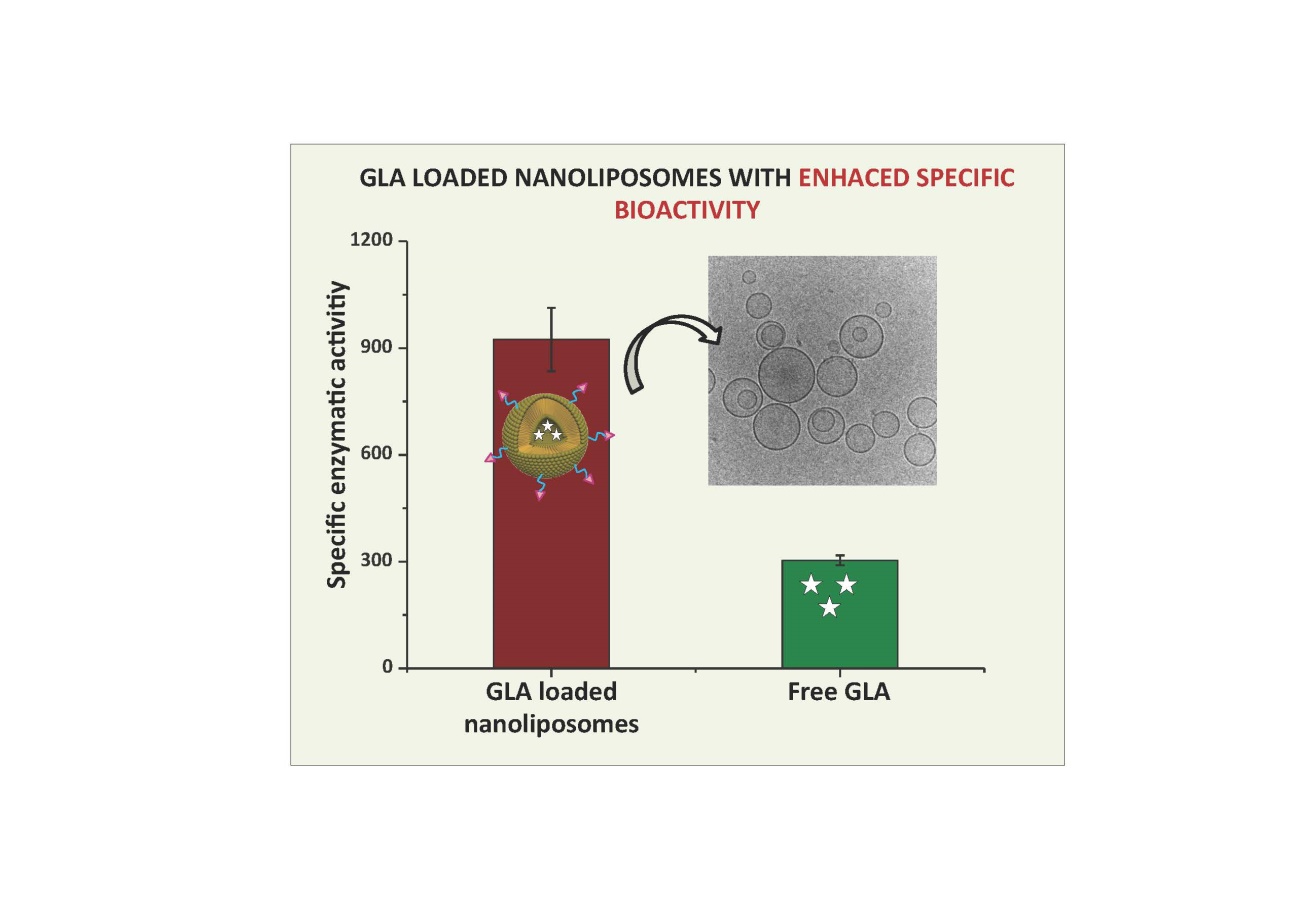
U26-E02. -NMR microscopy system for imaging Bruker 14T
- Functional and metabolic studies in cells, tissues and animal models. Coils 2mm, 5mm and 10mm. Image of 1H, 13C and 31P.
- Microcamera for its use in the NM R equipment for:
- The simultaneous determination of structural images (dimensions and sections of 50 μm and less)
- Metabolic images (voxel sizes < 200 μm) in model systems.