Nanoparticles to eradicate Cancer Stem Cells
Colorectal cancer (CRC) has a high prevalence worldwide and resistance to conventional chemotherapies and tumor relapse are usually related with a population of cells with malignant properties – Cancer Stem Cells (CSC).
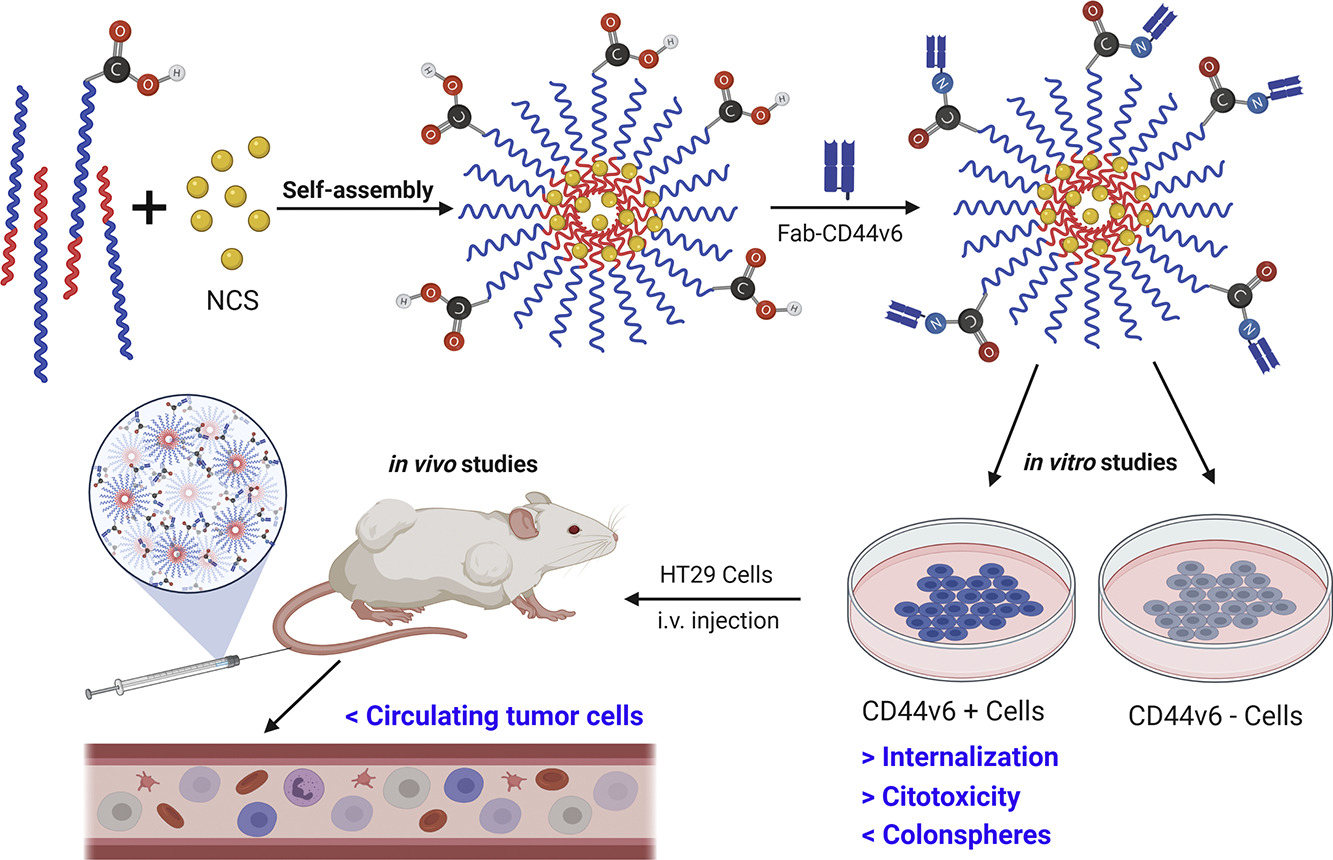
Scientists of CIBER-BBN and VHIR have led a research with the goal not only to treat the primary CRC, but also eradicate CSC. For both purposes, the use of nanoparticles (NP) is a useful strategy. These “bullets” carrying a drug in its core, are able to reach tumor tissue due to its small size. Cancer cells, and in particular CSC, present at their surface receptors that could be specifically recognized by molecules used to decorate NP, driven the drug of interest to these cells. In this work we developed a type of NP decorated with an antibody fragment that specifically recognize the receptor CD44v6, which is overexpressed in CSC and was previously demonstrated to be present in patients with metastasis and poor-prognosis. Moreover, researchers have encapsulated Niclosamide (NCS), a drug that demonstrated efficacy against breast CSC, inside their NP. NP increased the efficacy of NCS and accumulated in the tumors reducing its systemic exposure and increasing safety. Most importantly, the developed system significantly reduce circulating tumor cells, precursors of metastasis, reducing CSC malignancy.
This system has the potential to create a new therapeutic approach that could bring a new hope for CRC treatment and prevention of cancer relapse.
The work has been developed at the group of CIBBIM-Nanomedine_Drug Deliver & Targeting of Vall d’Hebron Institute of Research (VHIR) and CIBER-BBN, in collaboration with Bruno Sarmento (University of Porto, Portugal) and Marika Nestor (Uppsala University, Sweden) that helped to developed the NP and the targeting antibody, respectively. In vivo assays on the safety and efficacy of the NPs were conducted thanks to the contribution of the FVPR/U20 of ICTS-Nanbiosis.
Article of reference
Fernanda Andrade, Diana Rafael, Mireia Vilar-Hernández, Sara Montero, Francesc Martínez-Trucharte, Joaquin Seras-Franzoso, Zamira V.Díaz-Riascos, Ana Boullosa, Natalia García-Aranda, Patricia Cámara-Sánchez, Diego Arango, Marika Nestor, bane Abasolo, Bruno Sarmento, Simó SchwartzPolymeric micelles targeted against CD44v6 receptor increase niclosamide efficacy against colorectal cancer stem cells and reduce circulating tumor cells in vivo Journal of Controlled Release Volume 331, 10 March 2021, Pages 198-212 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.022