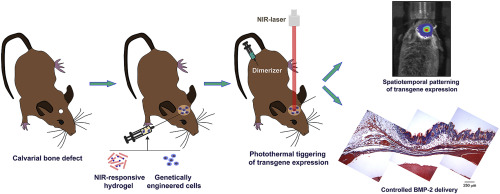
NANBIOSIS U9 Synthesis of Nanoparticles Unit has participated in a research carried out bu researchers of CIBER-BBN group FIOBI-HULP at Hospital de la Paz, led by Nuria Vilaboa. reclently published in the scientific journal Biomaterials The researchers have used transgenic cells, which are incorporated into the scaffolding, to regulate the physiological production of bone growth factors and induce the osteoinduction process.
Achievement of spatiotemporal control of growth factors production remains a main goal in tissue engineering. In the present work, we combined inducible transgene expression and near infrared (NIR)-responsive hydrogels technologies to develop a therapeutic platform for bone regeneration. A heat-activated and dimerizer-dependent transgene expression system was incorporated into mesenchymal stem cells to conditionally control the production of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Genetically engineered cells were entrapped in hydrogels based on fibrin and plasmonic gold nanoparticles that transduced incident energy of an NIR laser into heat. In the presence of dimerizer, photoinduced mild hyperthermia induced the release of bioactive BMP-2 from NIR-responsive cell constructs. A critical size bone defect, created in calvaria of immunocompetent mice, was filled with NIR-responsive hydrogels entrapping cells that expressed BMP-2 under the control of the heat-activated and dimerizer-dependent gene circuit. In animals that were treated with dimerizer, NIR irradiation of implants induced BMP-2 production in the bone lesion. Induction of NIR-responsive cell constructs conditionally expressing BMP-2 in bone defects resulted in the formation of new mineralized tissue, thus indicating the therapeutic potential of the technological platform.
Thanks to the participation of NANBIOSIS U9 Synthesis of Nanoparticles Unit it has been possible to explore the use of gold plasmonic nanoparticles, capable of absorbing light in the near-infrared (NIR) area and converting it into heat
Article of reference:
Sánchez-Casanova, S., Martin-Saavedra, F.M., Escudero-Duch, C., Falguera Uceda, M.I., Prieto, M., Arruebo, M., Acebo, P., Fabiilli, M.L., Franceschi, R.T., Vilaboa, N. Local delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from near infrared-responsive hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 241:119909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119909
Researchers of NANBIOSIS U3 Synthesis of Peptides Unit of CIBER-BBN at IQAC-CSIC, led by Miriam Royo, have published an article in the scientific journal ACS Omega that develops a method for the production of cholesterol conjugates to peptide ligands through polyethylene glycol (ND-PEG) not dispersed through a non-hydrolyzable bond.
The developed methodology allows to generate stable, highly pure and well defined Chol-PEG compounds, linked to different lengths of PEG from 4 to 20 units of ethylene oxide through an ether bond. These Chol-PEG compounds were conjugated with different peptides, such as cyclic peptide (RGDfK), gluturation and a Tf1R peptide ligand, preserving the oligomeric purity of the precursors, as demonstrated by analysis by HRMS and NMR. This method allows the systematic synthesis of stable, high-purity Chol-PEGs, bypassing the use of activation groups at each elongation step and thus reducing the number of synthesis steps.
The use of Chol-PEG conjugates has increased in recent years as a component of nanoformulations for applications such as drug administration or imaging systems, due to the ability of Chol to insert into artificial and cell membranes. This ability facilitates the stability of nanovesicles, such as liposomes or others, and entry into cells.
The synthesis of the peptides used in this work was carried out in Unit 3 of NANBIOSIS – ICTS Peptide Synthesis Unit and was developed within the framework of the HORIZON 2020 Smart4Fabry project.
Article of referrence:
Synthesis of Stable Cholesteryl–Polyethylene Glycol–Peptide Conjugates with Non-Disperse Polyethylene Glycol Lengths. Edgar Cristóbal-Lecina, Daniel Pulido, Pau Martin-Malpartida, Maria J. Macias, Fernando Albericio, and Miriam Royo. ACS Omega 2020 5 (10), 5508-5519 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00130

In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, several research infrastructures (RIs) NANBIOSIS among them, have set up specific services, such as rapid or fast track access, to allow researchers to obtain results as soon as possible.
The Association of European-Level Research Infrastructures Facilities (ERF-AISBL), collects the relevant information about the initiatives on a dedicated website.
NANBIOSIS provides rapid access for COVID-19 research. The ICTS offers preclinical stages services of biomedical product development, specifically, synthesis and preparation of biomolecules like antibodies, peptides, recombinant proteins, oligonucleotides for diagnostic therapeutic and prophylactic purposes.

Rosa Villa Sanz, the Scientific Director of NANBIOSIS U8 Micro– Nano Technology Unit was appointed group leader the CIBER during the last meeting of the Permanent Commission of CIBER-BBN, replacing Prof. Jordi Aguiló.
Rosa Villa Sanz, graduated in Medicine from the University of Barcelona and has a doctorate from the Autonomous University of Barcelona in 1993 and a specialist in Nuclear Medicine (MIR-Hospital de Bellvitge-Barcelona), is a scientific researcher at the CSIC and leader of the Biomedical Applications Group of the Barcelona Institute of Microelectronics (CSIC), whose main research interests are the design and manufacture of Micro and Nano Systems for Biomedical Applications.
Prof. Villa has participated in more than 30 national and European projects, being a principal researcher in 10 of them, she has obtained the approvals by the Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Devices (AEMPS) for the conduct of 4 clinical trials in collaboration with pharmaceutical companies and clinical groups and is the founder of a spin-off (Barcelona Liver Bioservice SL). Rosa Villa also directs a consolidated research group recognized by the Agència de Gestió d’Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca since 2014 (Bio-Micro-Nano-Systems group [2019 SGR 988]) and since 2016 co-directs the BioMEM TECNIO group of the Generalitat de Catalunya. Rosa Villa is Scientific of NANBIOSIS Unit 8 since the creation of NANBIOSIS.

Prof. Laura Lechuga, Scientific Director of NANBIOSIS U4 Biodeposition and Biodetection Unit of CIBER-BBN and ICN2-CSIC, who is coordinating the European proyect CONVAT for rapid diagnosis and monitoring of COVID ー 19, will be one of the speakers at the webinar organized next tuesday, 16 by the Young Academy of Spain, (JAE) about How Spanish science is contributing to the fight against COVID-19.
The talk by Prof Lechuga is titled “COVIDー 19 diagnosis: advantages and limitations of different techniques”
Global Young Academy (GYA) was created in 2010 at the initiative of young scientists and researchers from around the world who met in 2008 and 2009 during the “Annual Meeting of the New Champions”, known as “Summer Davos”. One of the objectives of the GYA is to promote the creation of National Young Academies around the world. JAE was created in march 2019 with the aim of representing and giving visibility to young scientists, preferably from the field of experimental sciences. The profile of the members of this Academy will coincide with the average of 40 years of age and 12 years from the attainment of the title of doctor, since a young scientist is understood as one who has reached maturity and is in the phases initials of his independent research career. Jesús Martínez de la Fuente, Principal Investigator of a CIBER-BBN group is Member of the Governing Board of the Young Academy of Spain.

Electrophoresis apparatus with several vertical and horizontal cuvettes for agarose and polyacrylamide (PAGE) gel electrophoresis.
UV-Visible and luminometer Reader used in luciferase and MTT assays
This service is dedicated to the custom synthesis of modified nucleotides such as nucleoside monophosphates or triphosphates as well as special phosphoramidites or functionalized solid supports functionalized with small molecules resistant to ammonia deprotection for the preparation of oligonucleotide conjugates.
Special nucleotides for oligonucleotide synthesis
For those services identified as outstanding, at least 20% of their capacity is open under competitive access. See Annex 1 of ACCESS PROTOCOL (provided by Nanbiosis) for details on % of openness for each service
Customer benefits
The service benefits from the 40-years’ experience of the researchers participating in the service with hundreds of scientific communications on improving the methodology used for the synthesis of modified oligonucleotides. This includes a range of modified nucleotides and terminal modifications not available in other services. In addition, the service can develop customized solutions for molecules not covered in the bibliography.
Target customer
The primary audience are research groups and companies involved in gene therapy, gene silencing and the development of nucleic acid-based diagnostic tools.
References
1) “Oligonucleotides containing 1’-aminomethyl or 1’-mercaptomethyl-2’-deoxy-D-ribofuranoses: Synthesis, purification, characterization and conjugation with fluorophores and lipids”. Martín-Nieves, V. et al. Bioconjugate Chem, 32, 350-366 (2021).
2) “Efficient bioactive oligonucleotide-protein conjugation for cell-targeted cancer therapy”. Aviñó, A. et al. Chemistry Open, 8, 382-387 (2019).
3) “Thioctic acid derivatives as building blocks to incorporate DNA oligonucleotides onto gold nanoparticles”. Pérez-Rentero, S. et al. Molecules, 19, 10495-10523 (2014).
This service is dedicated to the custom synthesis of oligonucleotide conjugates including oligonucleotides carrying lipids, amino acids, peptides or carbohydrates. In addition, they may include other modifications such as phosphorothioate linkages, 2’-O-methyl-RNA, 2’-O-MOE-RNA, 2′-F-RNA, Locked nucleic acids (LNA), modified nucleotides. The oligonucleotides will be prepared in 1 micromol scale. In most cases, the preparation of the conjugates will require the preparation of oligonucleotides carrying reactive groups such as; amino or thiol groups, which will be subjected to a post-synthetic modification. Purification and characterization will include reversed-phase HPLC analysis and mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF).
Modification of oligonucleotides during and post synthesis to meet user requirements:
Customer benefits
The service benefits from the 40-years’ experience of the researchers participating in the service, with hundreds of scientific communications on improving the methodology used for the synthesis of modified oligonucleotides. This includes fatty acid derivatives, amino acids, cell penetrating peptides and carbohydrates not available from other services. In addition, the service can develop customized solutions for molecules not addressed in the bibliography.
Target customer
The primary audience are research groups and companies working on gene therapy and gene inhibition in the early stages of preclinical development.
References
1) “Aptamer-peptide conjugates as a new strategy to modulate human α-thrombin binding affinity”. Aviñó, A. et al. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (General subjects), 1863, 1610-1630 (2019).
2) “Synthesis of oligonucleotides carrying amino-lipid groups at the 3’-end for RNA interference studies”. Grijalvo, S. et al. J. Org. Chem., 75, 6806-6813 (2010).
3) “Synthesis and evaluation of 3’ oleyl-oligonucleotide conjugates as potential cellular uptake enhancers”. Navarro, N. et al. SYNLETT, in press (2024). doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1751528.
