Design of parenteral MNP-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by a low-energy emulsification approach as theragnostic platforms for intravenous or intratumoral administration
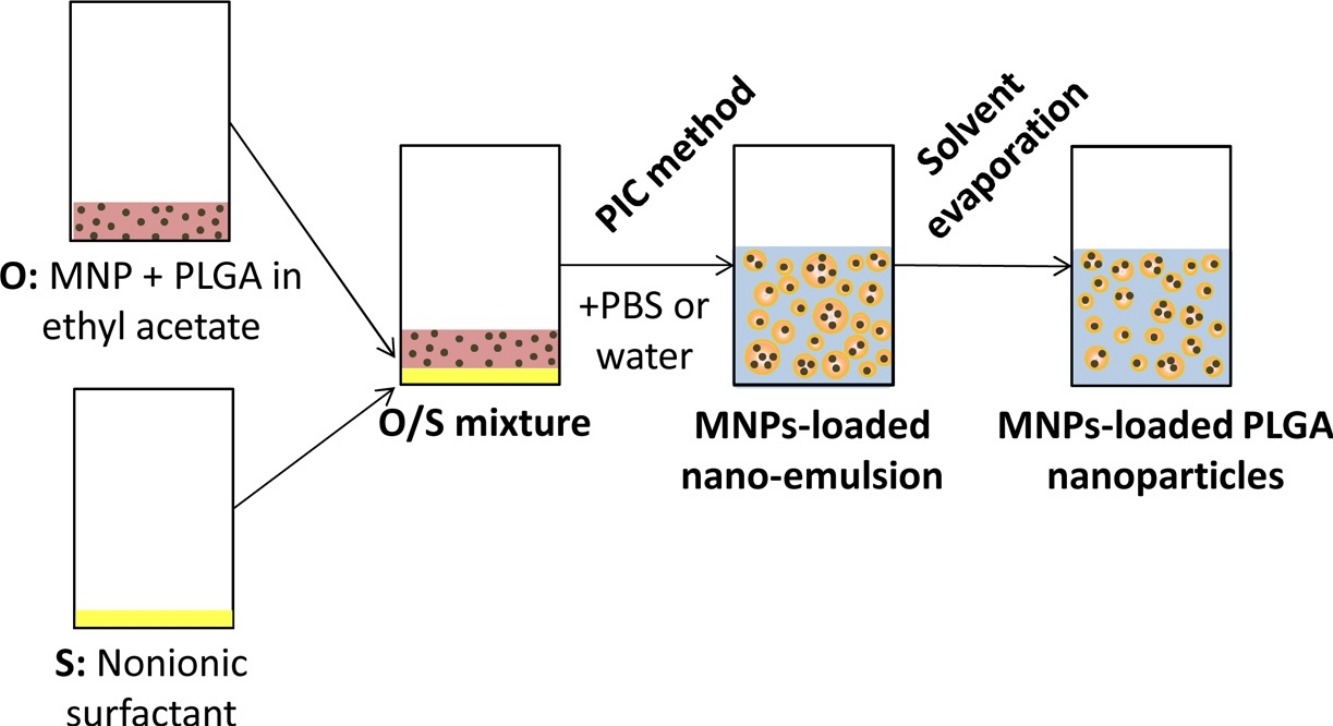
Encapsulation of magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) into PLGA nanoparticles has been achieved by nano-emulsion templating using for the first time both, a low-energy emulsification method as well as biocompatible components accepted for pharmaceuticals intended for human use. The incorporation of MNP by nano-emulsion templating method proposed in this work has been investigated in two different systems applying mild process conditions and is shown to be simple and versatile, providing stable MNP-loaded PLGA nanoparticles with tunable size and MNP concentration. MNP-loaded PLGA nanoparticles showed sizes below 200 nm by DLS and 50 nm by TEM, and mean MNP loading per PLGA nanoparticle of 1 to 4, depending on the nanoparticle dispersion composition. Physical-chemical features suggest that the MNP-loaded PLGA nanoparticles obtained are good candidates for intravenous or intratumoral administration.
The equipment of Dynamic Light Scattering (Dynamic Light Scattering) of NANBIOSIS Unit 12 has been used to determine the size distribution of polymer particles and Microscopy with Hyperspectral Analysis (Hyperspectral enhanced dark field microscopy) to detect the encapsulation of magnetic nanoparticles in polymer particles.
Article of reference:
Graphical abstract: Schematic representation of the preparation process of Fe3O4 MHighlightsN P-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nano-emulsion templating.