Methods for the In Vitro Characterization of Nanomedicines —Biological Component Interaction
An interesting article has been recently published, in the journal Personalized Medicine In the context of a public-private collaboration between Cristina Fornagera of Sagetis-Biotech and Conxita Solans, Scientific Director of Unit 12 of NANBIOSIS
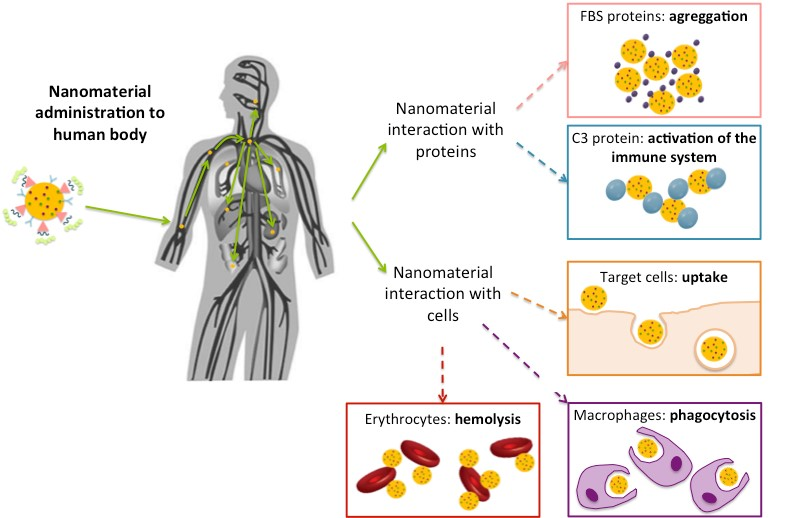
This review summarizes the main techniques used to assess the interaction of nanomedicines with biological systems, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. The translation of knowledge from novel designed nanosystems at a research laboratory scale to real human therapies is usually a limiting or even a final point due to the lack of systematic studies regarding two aspects: nanoparticle interaction with biological components and nanoparticle cytotoxicity.
For further information: