U2-S08. Inmunochemical methods development
Inmunochemical methods development
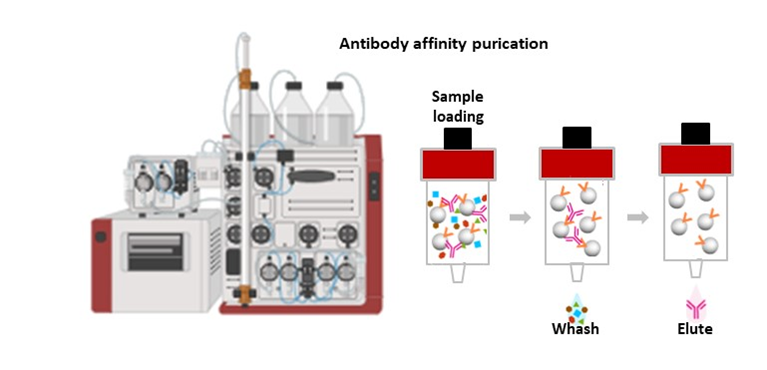
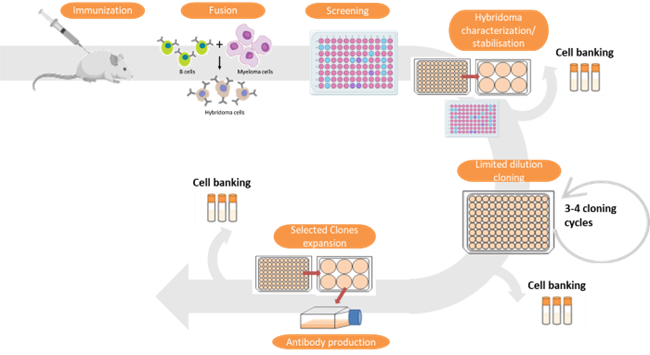
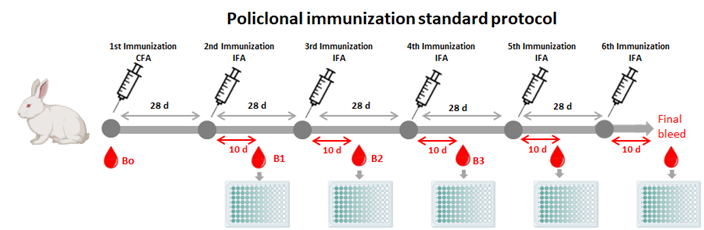
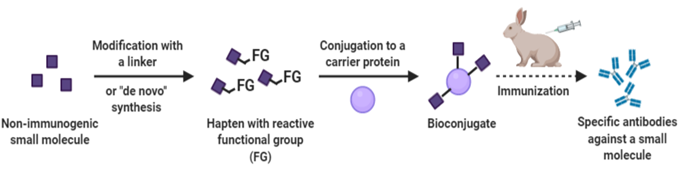
The service offers custom tailored immunoassay development. It involves designing and optimizing assays for detecting specific analytes (such as proteins, antibodies, or other biomolecules) in biological samples. The service includes identifying necessary reagents, establishing assay parameters, and validating the assay’s performance.
Customer benefits
- Tailored Solutions: By utilizing our custom tailored immunoassay development service, customers gain access to highly specialized expertise and resources, resulting in the creation of assays optimized for their unique requirements.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: The service ensures optimal sensitivity, allowing for the detection of analytes at low concentrations.
- Time and Cost Savings: Outsourcing immunoassay development to experts saves time and resources compared to in-house development.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous validation ensures reliable results, enhancing confidence in research outcomes.
Target customer
- Research Institutions: Universities, research centers, and laboratories engaged in biomedical research.
- Biotech Companies: Organizations involved in drug discovery, diagnostics, and therapeutic development.
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Those working on antibody-based therapies or vaccines.
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals and clinics conducting specialized research.
- Food & Environmental Quality Control Companies: Entities involved in:
- Food Contaminant Detection: Developing antibody-based
tests for identifying foodborne pathogens and toxins. - Environmental Contaminant Detection: Creating antibody-based assays for detecting environmental pollutants in air, water, and soil.
- Food Contaminant Detection: Developing antibody-based
Additional information
Selected references:
- G. Colom, A. Hernández-Albors, J. Barallat, A. Galan, A. Bayes-Genis, J.-P. Salvador, M.-P. Marco. A multiplexed immunochemical microarray for the determination of cardiovascular disease biomarkers. Microchim. Acta, 191, 54, 2023.
- C. Adrover-Jaume, A. Clemente, B. Rodríguez-Urretavizcaya, L. Vilaplana, M.-Pilar Marco, E. Rojo-Molinero, A. Oliver, R. de la Rica. A paper biosensor for overcoming matrix effects interfering with the detection of sputum pyocyanin with competitive immunoassays. Microchim acta, 190, 441, 2023.
- E. Montagut, J. Raya, M.-T. Martín Gómez, L. Vilaplana, B. Rodríguez- Urretavizcaya, M.-P. Marco. An Immunochemical Approach to detect the Quorum Sensing-Regulated Virulence Factor 2-Heptyl-4- Quinoline N-Oxide (HQNO) produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. Microbiol. Spect., 10(4), 1-12, 2022.
- E. Montagut, G. Acosta, F. Albericio, M. Royo, G. Godoy-Tena, A. Lacoma, C. Prat, J.-P. Salvador, M.-P. Marco. Direct Quantitative Immunochemical Analysis of the Autoinducer Peptide IV (AIP-IV) for Diagnosing and Stratifying Staphylococcus aureus infections. ACS Infect. Dis., 8(3), 645-656, 2022.
- B. Rodriguez-Urretavizcaya, N. Pascual, C. Pastells, M. T. Martin-Gomez, Ll. Vilaplana, M.-P. Marco. Diagnostic and Stratification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infected Patients by Immunochemical Quantitative Determination of Pyocyanin from Clinical Bacterial Isolates. Frontiers in Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 11, 786929, 2021. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.786929